Publications
Click here for an overview of my PhD research.
Through my objective of solving optimization problems under uncertainty in energy management, I explore, leverage, and enhance techniques in optimal transport, machine learning (mostly RL), convex optimization, and stochastic optimization algorithms.
I have thoroughly worked on the Wasserstein barycenter problem and proposed several extensions to the original formulation. I developed state-of-the-art algorithms to solve these problems and established rigorous mathematical guarantees for each of them.
Additionally, I tackled dimension reduction in the context of the nested distance—a generalization of the Wasserstein distance—to enable the application of classical methods to large-scale multistage problems.
Finally, I investigated the integration of reinforcement learning and stochastic optimization in a real-world industrial setting.
All of my research is supported by open-source code, and several contributions have been incorporated into industrial software.
Journal papers
| Mimouni, D., Malisani, P., Zhu, J., & de Oliveira, W. (2024). Computing Wasserstein Barycenter via operator splitting: the method of averaged marginals. DOI: 10.1137/23M1584228. In SIAM Journal on Mathematics of Data Science (SIMODS). (We have made, using AI, a song describing the method (MAM). You may check it here.) This work introduces a new algorithm for computing exact Wasserstein barycenters — for both free and fixed support — in balanced and unbalanced settings. The approach leverages the Douglas-Rachford operator splitting scheme, demonstrating that the iterative steps are computationally efficient. Link: Paper / ResearchGate / paper PDF / github. |
| Mimouni, D., de Oliveira, W., Sempere, G. M. (2025). On the Computation of Constrained Wasserstein Barycenters. Accepted in Pacific Journal of Optimization for a special issue dedicated to Professor R. Tyrrell Rockafellar on the occasion of his 90th birthday. This work extends my previous method for computing the Wasserstein barycenter using the Douglas-Rachford splitting scheme. In this study, a constraint is imposed on the barycenter in the original problem, and efficient methods are developed to solve it in both convex and non-convex settings. Link: paper PDF / github, also visit. |
| Mimouni, D., Malisani, P., Zhu, J., & de Oliveira, W. (2024). Scenario Tree Reduction via Wasserstein Barycenters. Submitted to Annals of Operations Research. The method, based on the nested distance, proposed by Kovacevic and Pichler is the most accurate for reducing scenario trees, but its slow execution has limited its practical use. In this work, we show that the method can be significantly accelerated by reformulating one of its steps as an optimal transport problem, solvable with state-of-the-art algorithms. The resulting algorithm is nearly ten times faster, making it suitable for industrial applications. Link: website / paper PDF / github. |
| Currently working on Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Distributionally Robust Optimization (DRO) to tackle multi-stage stochastic optimization problems. This work will be submitted to IEEE Transaction journal. The goal of this work is to develop a concrete solution for an Energy Management System requiring multistage decision-making. This project will soon be integrated into IFPEN's EMS-lab@ifpen solver. Link: paper PDF / github. |
International Conferences
| Mimouni, D., Malisani, P., Zhu, J., & de Oliveira, W.: How Optimal Transport can make multi-stage decisions sharper : Boosting scenario tree algorithms (2025). Presentation during the XIIth Conference on Stochastic Programming (ICSP 2025) Link: slides / Presentation (video) on demand. |
| Mimouni, D., Malisani, P., Zhu, J., & de Oliveira, W. (July 2025). Optimization framework to solve Energy Management System problems: Reinforcement Learning vs Stochastic Programming. Presentation during the 2025 International Conference on Continuous Optimization (ICCOPT 2025) Link: slides / Presentation (video) on demand. |
| Mimouni, D.(2023). Advances in Variational Analysis and Nonsmooth Optimization: Computing Wasserstein Barycenter via Operator Splitting: the Method of Averaged Marginals, July 2024. Presentation during the 25th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming (ISMP 2025) Link: slides / Presentation (video) on demand. |
| de Oliveira, W., Mimouni, D.(2024). New Approach to Optimal Transport problems, 2024 Presentation at EUROPT 2024 Link: slides. |
French Conferences
| Mimouni, D.(2024). Scenarios methods in stochastic control and applications: Boosting Scenario Tree Reduction, November 2024. Presentation during the The Gaspard Monge Program for Optimization, Operations Research and their interactions with Data Sciences (PGMO) Link: slides / Presentation (video) on demand. |
| Mimouni, D.(2023). A new approach for computing Wasserstein Barycenter via operator splitting in the classical balanced setting, Nov 2023. Presentation during the PGMO days Link: slides / Presentation (video) on demand. |
| Mimouni, D.(2023). About the Computation of Wasserstein Barycenters, April 2023. Presentation during the CIROQUO conference Links: Poster. |
PhD Report
| Mimouni, D.(2025). Multistage Stochastic Optimization: From Optimal Transport-Based Scenario Tree Reduction to Robust Optimization. I defend my thesis at Mines Paris (VI). Jury: Prof. Alois PICHLER, Prof. Franck IUTZELER, Prof. Michel DE LARA, Dr. Delphine BRESCH-PIETRI, Dr. Welington DE OLIVEIRA, Dr. Paul MALISANI, Dr. Jiamin ZHU. The official arxiv in french and in english is here. Links: Report / Slides / Outreach booklet in french / Presentation (video) on demand. 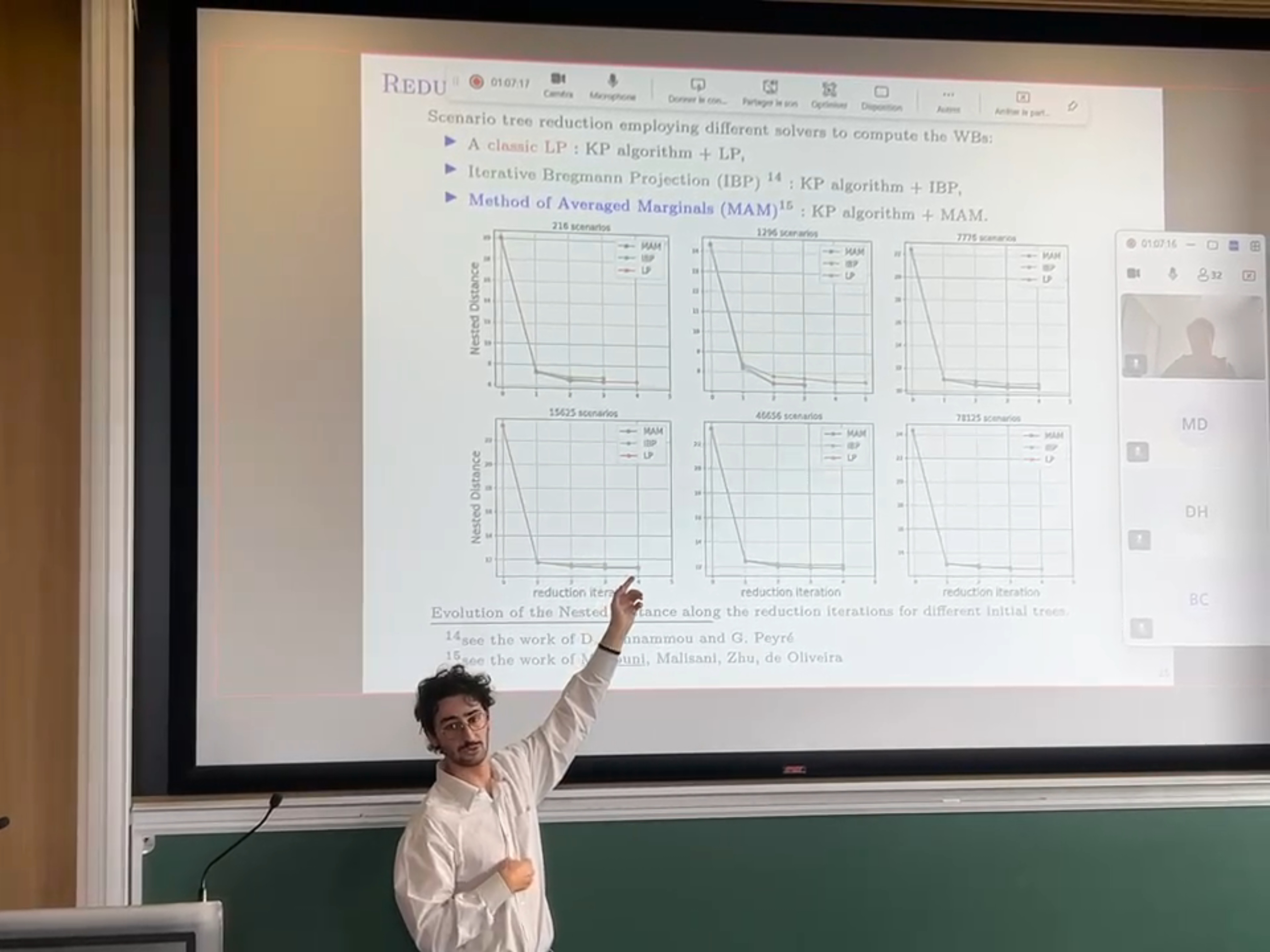 |
